Table of Contents
Master Data Management (MDM)
What is Master data ?
Master data is a collection of common, core entities along with their attributes and their values—that are considered critical to a company’s business, and that are required for use in two or more systems or business processes. These entities represent the slowly changing part of the business’ data and usually fall into four categories:
- Parties: represents all parties the enterprise conducts business with such as customers, prospects, individuals, suppliers, partners, etc.
- Places: represents the physical places and their segmentations such as geographies, locations, subsidiaries, sites, areas, zones, etc.
- Things: usually represents what the enterprise actually sells such as products, services, packages, items, financial services, etc.
- Financial and Organizational: represents all roll-up hierarchies used in many places for reporting and accounting purposes such as organization structures, sales territories, chart of accounts, cost centers etc.
Master data challenges
- Continuous changes to data: Introduction of a new product, the addition of a new sales representative or new product pricing. These are everyday events in most enterprises and very cumbersome if done manually.
- Huge Volumes: According to the multiple studies 50 percent of enterprises separately maintain master data in 11 or more source systems. Management task in an enterprise with thousands of changes across 11 or more systems every month.
- Incomplete data: Since master data is usually created manually hence problem of data incompleteness encountered often.
- Duplicate data across systems: Due to lack of data governance and control processes duplicate data exists in multiple systems.
- Lack of trusted source for data: No synchronization among disparate systems hence each systems considers it’s data as trusted source.
What is MDM
Master Data Management (MDM) is the controlled process by which the master data is created and maintained as the system of record for the enterprise.
- MDM is implemented in order to ensure that the master data is validated as correct, consistent, and complete.
- MDM has the objective of providing processes for collecting, aggregating, matching, consolidating, quality-assuring, persisting and distributing such data throughout an organization to ensure consistency and control in the ongoing maintenance and application use of this information.
- MDM is a Business function.
Typical MDM functions
- Data cleansing, enrichment
- Validation
- Search
- Match
- Merge
- Trust
- Publish
Why MDM ?
- A single, consolidated bill saves money and improves customer satisfaction.
- Sending the same marketing literature to a customer from multiple customer lists wastes money and irritates the customer.
- Before you turn a customer account over to a collection agency, it would be good to know if they owe other parts of your company money or, more importantly, that they are another division’s biggest customer.
- Stocking the same item under different part numbers is not only a waste of money and shelf space, but can potentially lead to artificial shortages.
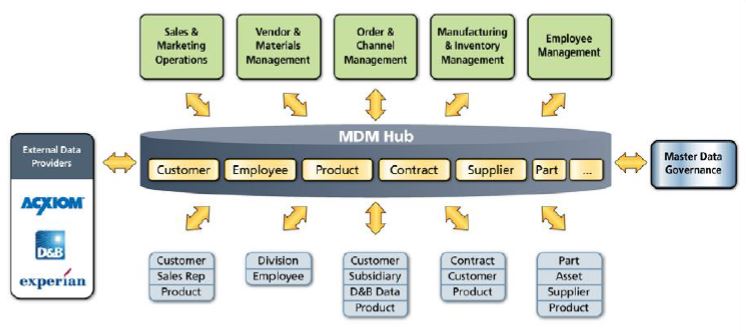
MDM data flow
Architecture principles of MDM
Core architecture for guiding MDM solution development
- The MDM solution should provide the ability to decouple information from enterprise applications and processes to make it available as a strategic asset for use by the enterprise.
- The MDM solution should provide the enterprise with an authoritative source for master data that manages information integrity and controls the distribution of master data across the enterprise in a standardized way that enables reuse. The primary motivation for this principle is to centralize the management of master data to reduce data management costs and improve the accuracy and completeness of that data.
- The MDM solution should provide the flexibility to accommodate changes to master data schema, business requirements and regulations, and support the addition of new master data. This improves the ability of a business to quickly respond to business changes that may require the addition of new master data elements or changes to existing master data.
- The MDM solution should be designed with the highest regard to preserve the ownership of data, integrity and security of the data from the time it is entered into the system until retention of the data is no longer required. The objective of this principle is to ensure that core business data that is critical to the success of the enterprise will be secure and to comply with privacy laws and regulations.
- The MDM solution should be based upon industry-accepted open computing standards to support the use of multiple technologies andtechniques for interoperability with external systems and systems within the enterprise. This will guide development of the architecture to remain open and flexible so it can easily integrate with a variety of vendor software that may already exist within the enterprise and any future unknown technologies.
- The MDM solution should be based upon an architectural framework and reusable services that can leverage existing technologies within the enterprise. This principle guides the architectural decisions to leverage existing investments in technologies such as those that facilitate connectivity and interoperability or information integration where it makes sense in order to implement a MDM Solution.
- The MDM solution should provide the ability to incrementally implement an MDM solution so that a MDM solution can demonstrate immediate value.