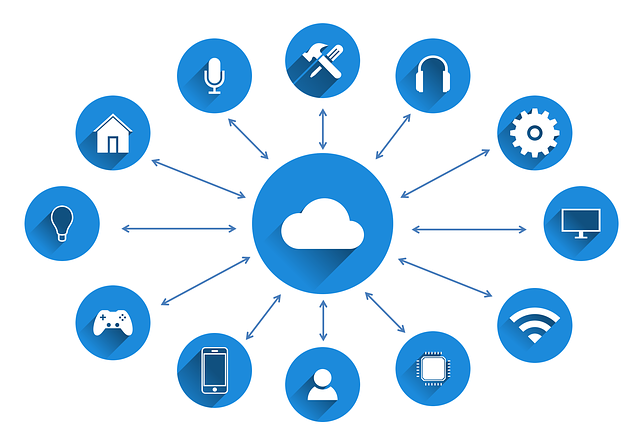
Cloud computing can be defined as a computing which is based on approach of sharing computing resources instead of configuring local servers or devices to host applications.
In terms of cloud computing, the word cloud (also phrased as “the cloud“) is used as a metaphor for “the Internet” so the phrase cloud computing means “a category of Internet-based computing,” in which a number of services — such as servers, storage and applications —are address the need of an organization’s for computers and devices, through the Internet.
Following Cloud Computing metaphor image explains the concept and overview.
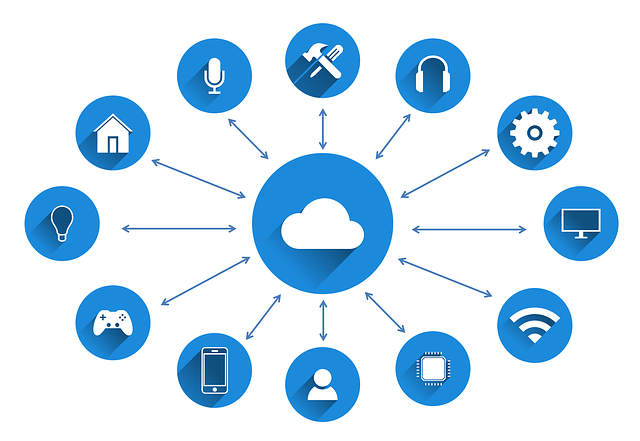
Table of Contents
Evolution and History of Cloud Computing
Traditional business applications – being very complicated and expensive – always be in daunting need of the amount and variety of hardware and software required to run. Also, as the Business applications is relevant to a single business unit – need a whole team of experts to install, configure, test, run, secure, and update them.
Cloud computing has evolved through a number of phases which include Grid and Utility computing, Application Service Provision (ASP), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
But the revolutionary concept of delivering computing resources through a global network is got momentum in the years of sixties.
With emerging demand and requirement – the rise of commercial networking wasn’t an easy task to implement, hence companies started have check on their business plan, business models and execution approach. All those boiled down to the fact that “Having huge financial backup, having solid support of investors, having huge base of consumers is not a guarantee of all time affluent business. To survive and excel there is always need of excellent business plan with continuous inspection and improvement scope into that”.
In the search for new options to reap the benefits of growing Internet exposure and its impact on worldwide users, many companies started to conceptualize a service model to deliver usable solutions and resources for the need of computing.
salesforce.come could be termed as the company who kicked-off the trend by pioneering the concept and delivering enterprise-class applications over a simple internet.
Next in 2002, Amazon joined the stream as Cloud Computing service provider with Amazon Web Services (AWS). This gave users ability to access storage, computation solutions and other apps through internet. In 2006 Amazon went further with Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), which basically lent space (on Amazon hosted machines) on their computers to store and run the Client’s own apps. It was an entire infrastructure which they delivered as service.
By 2009, gradually other companies like Google and Microsoft started offering the Cloud Computing Services.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing can be categorized in one of two ways, either based on the Location of the Cloud, or the Service type of the Cloud.
Based on Cloud Location, cloud computing can be classified as:
- Public
- Private
- Hybrid
- Community cloud
Based on Cloud Service Type, cloud computing can be classified as:
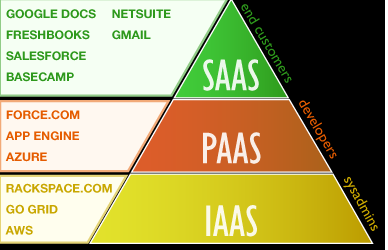
- IaaS (Infrastructure as Service)
- PaaS (Platform as Service)
- SaaS (Software as Service)
How the “cloud” Works ?
Any job performed and task executed in a machine is a feature of an application, say opening web browser and loading some site – surely, there are set of applications which are getting executed to load the web pages. So those set of applications are actually located on a remote machine which is owned by another company where the real storage and the software does not exist on end-user computer, but exist instead – on a cloud.
Like every other system has layers, so also Cloud has its own layers – usually known as:
- Front-end layer,
- Back-end layer, and
- Network layer – used to connected the end users’ devices.
On the front end of a cloud computing system there is:
- a client
- an application
- user interface
On the back end of the system, there are computers that run the applications
- servers (with a central server(s))
- data storage systems
Each application will have its own server, and a central server that monitors traffic on all other servers, and communicates through protocols. The software that is used in a cloud computing system, which allows computers to communicate, is known as Middleware.
As for the data storage, a cloud computing system must copy all data and store it at, at least, one other device. Thus, it requires twice the number of storage devices for the company that provides the service, or more. This is known as Redundancy.
The resources, or the electronic equipment – which is required to handle the data, are stored and placed in data centers, also known as Server Farms. All the digital information depends on these Server Farms.
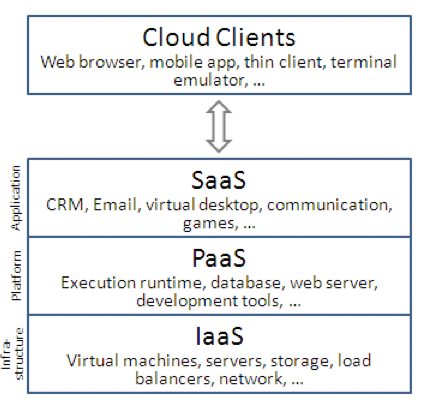
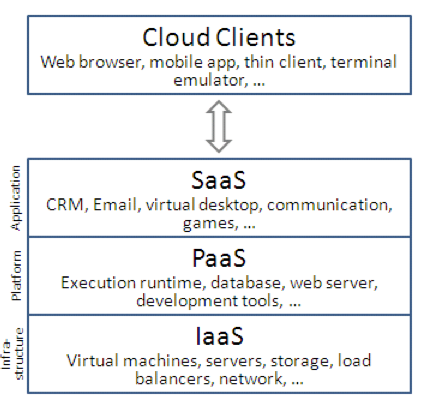
Need for Cloud Computing
Companies started to think for automated decision making system, which can perform complex operations and maintain the system, rather than relying of high man power. Hence, by adopting the Cloud, users can access the data from anywhere, at any time only at the cost of internet connection.
For any cloud service they are usually paid for, as and when they are being used but with regular hosting, it is paid for the server maintenance and the staff all of the time, and it is not sure if the service will always be optimal to your end users.
Hence, with the adoption of Cloud, users get many advantages such as:
- no stress of buying software licenses for each tool they need to install,
- hardware cost is brought down (data is stored and copied on the cloud),
- need computers with less processing power (without losing on the performance),
- save money on IT support, and on server and data storage space that usually requires high maintenance,
- can solve more complex problems easily and speedily, by using a grid of computers available on the cloud, instead of a single computer,
- Can grow their business as much as they like, without experiencing failures in the system due to the large number of customers.
Security Concerns and Mitigation
Securing data on internet is always a big concern, it needs to analyzed, planned and implemented the ways to stop an attacker to enter the cloud environment through any possible points of entry. Accessing insecure mobile phone to access the network, using a web application that has an embedded vulnerability, anything which is not protected – can be attacked, so also sharing of username, password of a database can sometimes lead to breach.
Securing the security perimeter of the traditional data center was made relatively straightforward with the help of firewalls and intrusion detection systems. When we traded terminals for PCs, anti-virus software helped keep those devices safe. But these security perimeter is just not enough for protecting the edge, certain steps has to be taken to ensure extra security.
- 1. Know who’s accessing what
People within your organization who are privileged users, – such as database administrators and employees with access to highly valuable intellectual property – should receive a higher level of scrutiny, receive training on securely handling data, and stronger access control. - Limit data access based on user context
Change the level of access to data in the cloud depending on where the user is and what device they are using. For example, a doctor at the hospital during regular working hours may have full access to patient records. When she’s using her mobile phone from the neighborhood coffee shop, she has to go through additional sign-on steps and has more limited access to the data. - Take a risk-based approach to securing assets used in the cloud
Identify databases with highly sensitive or valuable data and provide extra protection, encryption and monitoring around them. - Extend security to the device
Ensure that corporate data is isolated from personal data on the mobile device. Install a patch management agent on the device so that it is always running the latest level of software. Scan mobile applications to check for vulnerabilities. - Add intelligence to network protection
The network still needs to be protected – never more so than in the cloud. Network protection devices need to have the ability to provide extra control with analytics and insight into which users are accessing what content and applications. - Build in the ability to see through the cloud
Security devices, such as those validating user IDs and passwords, capture security data to create the audit trail needed for regulatory compliance and forensic investigation. The trick is to find meaningful signals about a potential attack or security risk in the sea of data points.
Adding a layer of advanced analytics – a security intelligence layer – brings all of this security data together to provide real-time visibility.
Leading Cloud Computing Vendors
AWS Cloud Computing
AWS is an IaaS cloud solution which provides on-demand delivery of IT resources via the internet based on pay-as-you-go pricing approach. AWS can be defined as collection of remote computing services, also called web services that together make up a cloud computing platform in a low cost environment. Numerous customers have joined the AWS community to use its solutions to build business. With AWS, public or private data can be stored, dynamic websites can be hosted, and data can be analyzed.
AWS Offerings:
- Website Hosting
AWS offers cloud website hosting solutions, where the website server and software is being used, paid for only what is being used.
- Backup and Recovery
- AWS provides a solution for storing information in any form, reducing the hardware maintenance.
- With this, we can keep multiple copies of the data, pay for what we use, can encrypt data to keep it safe.
- Archiving
- Disaster Recovery
- Development and Test
- Big Data
- High Performance Computing
- Databases
- Digital Marketing
- E-commerce
- Application Hosting
- Mobile Services
- Internet of Things
- Enterprise IT
- Content Delivery
- Health
- Gaming
Rackspace
Rackspace cloud is group of cloud computing product and services which include:
- Cloud Sites (PaaS)
It allows the user to host applications on horizontally scalable hardware infrastructure. It runs Windows/Linux application across numerous servers. It allows configuring of unlimited number of sites, databases etc.
- Cloud Files (Cloud Storage)
It is a cloud hosting service which provides unlimited online storage with upload bandwidth up files of size up to 5GB.
- Cloud Servers (IaaS – Virtual Private Servers)
It is cloud infrastructure service, which allows to deploy and create advanced and highly available architecture in hassle-free way. The “cloud servers” are virtual machines running on the Xen hypervisor for Linux-based instances, and Citrix XenServer for Windows and Linux instances.
Rackspace Cloud offers features of Flexibility, Scalability and Security.
Akamai
Akamai is one of the key service provider for Cloud Computing. Akamai supports mainly the following types:
- Cloud Storage Service (PaaS)
To support the need of string and managing the exponential growth of data by means of media files, server and sensor logs, digitized documents – Akamai offers Cloud Storage Service, in turn which helps to avail Savings, Scalability, Data Protection and Proximity to end users.
- Cloud Computing Infrastructure (IaaS)
Akamai offers the Cloud Computing Infrastructure to avail Virtualization, Automation, Self-service interfaces and Multi-tenancy. Akamai helps public and private cloud operators to deliver high performance cloud services throughout the word via any type of usage devices.
- Web Performance Solution (Saas)
Akamai offers a set of capabilities for a comprehensive, integrated collection of performance and reliability solution designed to meet the unique demands of delivering SaaS applications.
Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is cloud computing platform through which Google offers the very same infrastructure which Google uses for its own products like Search, YouTube etc. Google offers a huge range cloud based services via Google cloud platform, few of them are:
- Google App Engine – it is IaaS type of offering from GCP which enables launching Virtual Machines,
- Google Cloud Storage – enables storage over Google Cloud,
- Google Cloud Datastore – NoSQL data storage for non-rational data, including REST API,
- Google BigQuery – Data analysis tool which can process big datasets via SQL type queries in fraction of seconds.
Windows Azure
Windows Azure is can be termed as integrated operating system for cloud computing which caters the need of configuring and managing scalability of web application over the internet. Windows Azure provides both Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS). Windows Azure was temporarily called “Windows Cloud” at the time of launch in 2008.
The Azure OS is the key component which include:
- Distinguish Application
- Storage
- Service Layers for Virtualization
- Security
- Desktop Development Environment
Windows Azure has following key features to offer optimal performance with high availability:
- Automated Service Management (ASM) – which handles the updgradation of application keeping the performance of application intact.
- Load Balancing
- Caching
- Fault Tolerance
- Redundancy
Don’t forget to check out :
- What is Cloud Computing ?- Definition from Trenovision
- Cloud Computing Questions and Answers
- Cloud computing Quiz
- Cloud Computing – AWS Solved MCQ