What is Credit monitoring ? – Credit monitoring is carried out by the CRM area that is responsible for thedaily monitoring of the information made available in the limit control systemcredit, in order to ensure its integrity and accuracy.
As provided for in the Credit Risk Management Policies, the credit limitsare invariably reviewed annually and whenever there is any fact that changes theperception of risk that the Bank has in relation to the counterparty or in relation to the situation of the Marketplace.
Table of Contents
Credit control – overview
All the operator’s provide their services and collect revenue from the end customers to survive in the business. There may be two possible way to charge an end customer:
- In-Advance:An operator charges the customers in advance before providing the service. This leads to less customer satisfaction but operator is more secure from revenue point of view.
- In-Arrears:An operator put himself on risk and charges the customer at end of every month after providing required services. This leads to more customer satisfaction but operator is on a risk of collecting less revenue.
Why Credit control monitoring needed ?
- There is always a threshold up to what an operator can tolerate revenue loss associated with a particular customer same time there is a threshold of risk, an operator can take with a particular customer.
- For example, if a customer’s income is $10,000/month then operator can provide him their services very easily upto $1000 – $2000 but for the same operator it would be difficult to provide him a service which would cost almost $10,000/month because in such situation, it would be difficult for the customer to make monthly payment.
- Keeping the same concept, operators define different credit classes which they use to classify their customers and associate different credit and collection actions and reduce revenue loss.
What are Credit Classes ?
The credit class defines a category of the customer and associated risk of revenue can be taken with that customer. A credit class also defines which collections schedule is to be applied to the customer, should its owner fail to make the (undisputed) payments that are due.
All the Billing Systems provide facility to define various credit classes which can be assigned to different customers at the time of adding them into the system. Following are few examples of credit classes:
- VIP Credit Class:This can be assigned to VIP customers and would have very high value of credit limit.
- General Public Class:This is the most common credit class and would have almost $100 or $200 credit limit.
- Segment Specific Class:These classes can be defined based on different segments like police, military or bank officers etc. Operator can define credit limit based on their comfort.
There could be infinite number of credit classes defined based on the requirements and category of the customers.
What are Credit Control stages ?
There are mainly two stages where credit can be controlled for a particular type of customer category:
- Un-billed Usage Based:This is rating time control which is done by the Rating Processes. Here customer’s usage and total charges are checked against the assigned credit limit and if customer starts approaching towards the assigned credit limit, customer is informed about the same and after breaching the credit limit an appropriate action can be taken.
There are operators who would like to bar ( ie. temporarily stop) the services if customer is breaching the credit limit and they would be unbarred once the payment is done.
For example: Customer having a credit Limit of $200, will be informed on 80% of usage by a mean of SMS , on reaching threshold of 90% might be informed by mean of a remainder call etc., and when 100% credit limit has been reached, then Out going might be barred.
To control the credit, operators like to bar only outgoing calls in case of Voice and SMS usage but in case of data download, customer would not be able to perform any data download.
- Billed Usage Based:This is usually done after sending the invoices
To control the credit at rating time, it is important to keep rating as real time as possible. If usage is not being captured in real time and it is being rated after a long gap then there is a possibility that customers would have crossed their credit limit and legally customer may not be able to pay the amount beyond their assigned credit limits.
Credit Dunning
After an invoice is generated and dispatched to the customer, ideally, all customers will receive their bills and pay promptly. However, there may be some customers who do not pay their bills and there may be an unacceptable delay in paying the bill and hence the service providers must take some action need to remedy the situation and collect the outstanding balance due (called account receivable, abbreviated as A/R).
Collection is the process of chasing past due receivables on customer account. This usually involves sending notifications to the customer and taking appropriate actions in absence of due payments after the due date.
Billing Systems support dunning (receivables chasing) both at the invoice level where receivables are chased on an invoice by invoice basis or at the account level whereby all overdue amounts for an account, across several invoices, can be handled by a single dunning action.
Credit Collection Process and there dunning Models
The dunning model to be used for an account will be assigned on the basis of its credit class. A core collection process include following two items:
- Collections Aging Tracking:This is the process of tracking the customer invoices that have not been paid within the specified payment period due date. It deals with the “age of account receivables” for example, invoices that are 0-30 days overdue, 30-60 days overdue etc.
- Collections Actions:Collection action is the action that is performed when the account receivable reaches a particular age. For example, reminder messages to the customer to be mailed or recorded audio message should be played.
Soft Collection Actions – Dunning Notices:
- In the early stages of the collections process, the soft collection action will typically be to send a number of dunning notices which are simple reminder letters and requests for payment.
- After a number of dunning notices have been sent at various stages, other actions are typically scheduled. For example, you can specify that a customer services representative (CSR) should telephone the customer to ask why they have not paid.
Hard Collection Actions – Blacklisting
- If the initial attempts fail, then more aggressive actions can be taken like barring the services, or disconnecting the services or hot-lining (hot-lining is the process of re-directing all calls of delinquent customers to collections operator).
- If all the attempts to collect the dues fail then the service provider may write-off the account and marks the due amount as bad debt or may hand over (sell off) the account to a collection agency. Collection agencies work on a percentage of collected revenue. However, once the uncollected account invoices are sold off to a collection agency, the service provider is not allowed to work with the customer regarding the payments.
- Here write-off means, service provider (operator) clears the dues on behalf of the customer and close the account forever. This is done for accounting purpose otherwise it is a loss for the operator.
- The service provider maintains the history of the write off accounts also called blacklist customers so that they are not re-activated again and informs the credit checking/ reporting agencies about such accounts.
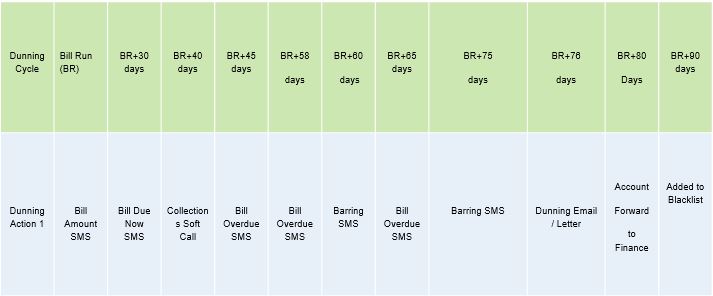
Sample collection Actions :


3 Replies to “Credit monitoring and Collections | Explained”
Comments are closed.